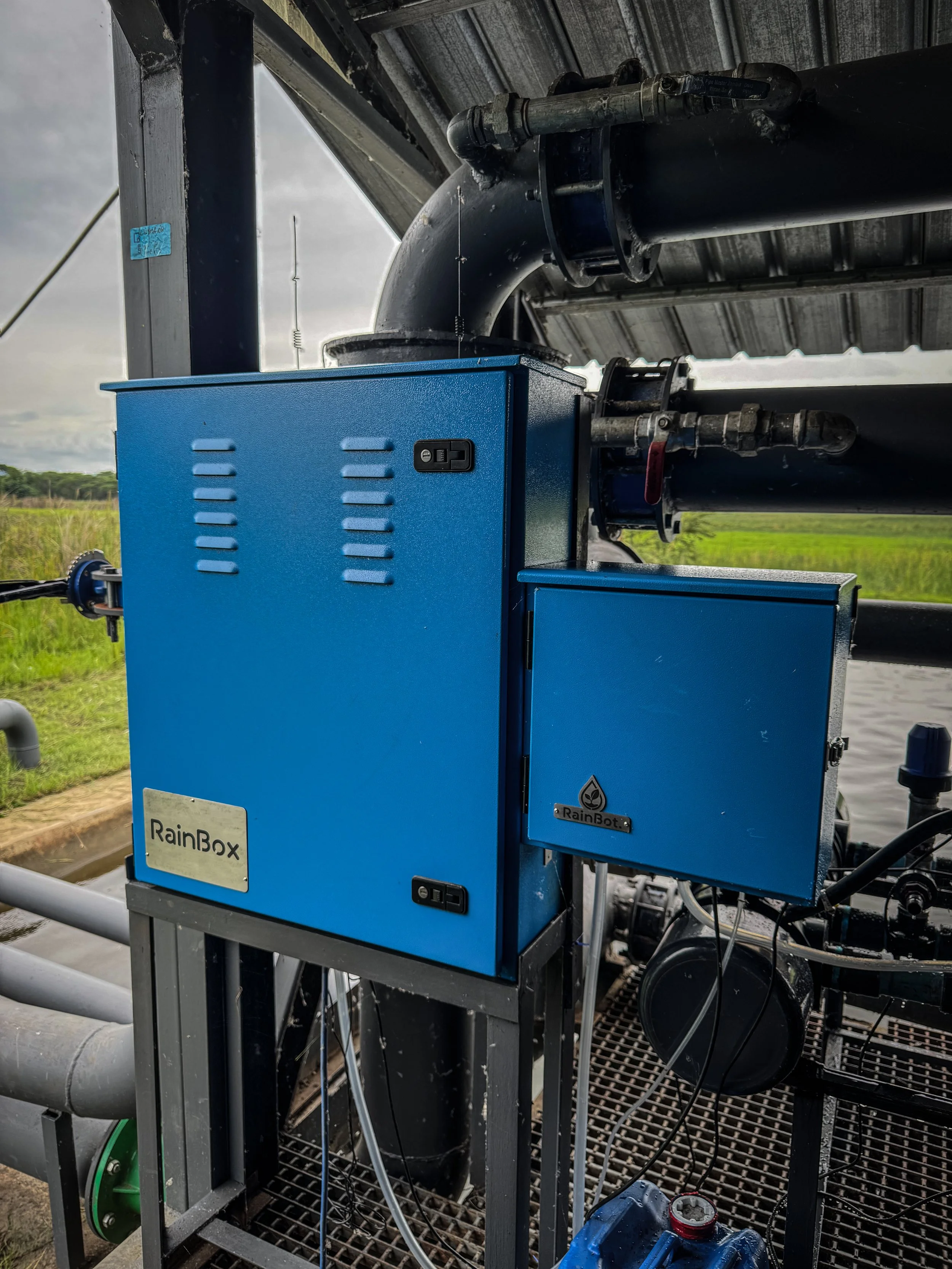
RAINBOX AOP – ADVANCED OXIDATION FOR HEALTHIER WATER, SOIL & CROPS
How It Works:
The Rainbox system treats the atmosphere via UV lamps, generating ozone and carbonic acid precursors. About 10% of the irrigation water is diverted through a Venturi injector, where the treated atmosphere is introduced. Then, 50% hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂) is injected at 1-2 ppm, triggering advanced oxidation reactions that:
Break down biofilms in irrigation lines
- Reduce water viscosity for better infiltration
- Increase dissolved oxygen, supporting root-zone microbes
- Free up bound minerals, improving soil fertility
- Reduce soil compaction, enhancing root development
- Improve water-holding capacity, optimizing moisture retention
🌿 Cation Balance: The Hidden Key to Soil Health
Understanding Cation Interactions
Soil fertility isn’t just about how much of a nutrient is present — it’s about how
nutrients interact. When sodium (Na⁺) dominates, it displaces critical cations like
calcium (Ca²⁺), magnesium (Mg²⁺), and potassium (K⁺), leading to:
• Compacted, tight soils
• Blocked nutrient uptake
• Salt stress in roots
• Poor water infiltration
This imbalance is a major reason for yield loss and long-term soil degradation.
💧 The Rainbox AOP Advantage:
Smart Water for Better Soil
The Rainbox AOP system uses advanced oxidation chemistry to restructure irrigation
water by:
Increasing the bioavailability of Ca²⁺, Mg²⁺, and K⁺
Reducing the activity and binding power of sodium
Preventing salt precipitation and biofilm buildup
Transforming harmful anions (like Cl⁻ and CO₃ ²⁻) into less reactive forms
Even though electrical conductivity (EC) may stay the same or increase, the water
behaves differently — and so does your soil.
📊 Field-Proven Results: CF Pivot Trial (2022–2023)
The CF Pivot field (potatoes and grain) was treated with Rainbox AOP water throughout
the 2023 season. Regular soil testing revealed dramatic improvements in cation ratios
and salt reduction: 0–6” Soil Layer
• Sodium (Na⁺) ↓ 57.3%
• Magnesium (Mg²⁺) ↓ 42.5%
• Chloride (Cl⁻) ↓ 60.7% 6–24” Soil Layer
• Sodium (Na⁺) ↓ 77.5%
• Magnesium (Mg²⁺) ↓ 52.2%
• Chloride (Cl⁻) ↓ 83.5%
These shifts indicate a strong displacement of sodium by calcium and
magnesium, allowing the soil to “breathe” again and nutrients to flow more freely.